Configure Rasterization
Below window will pop-up when ‘rasterization settings...’ is clicked.
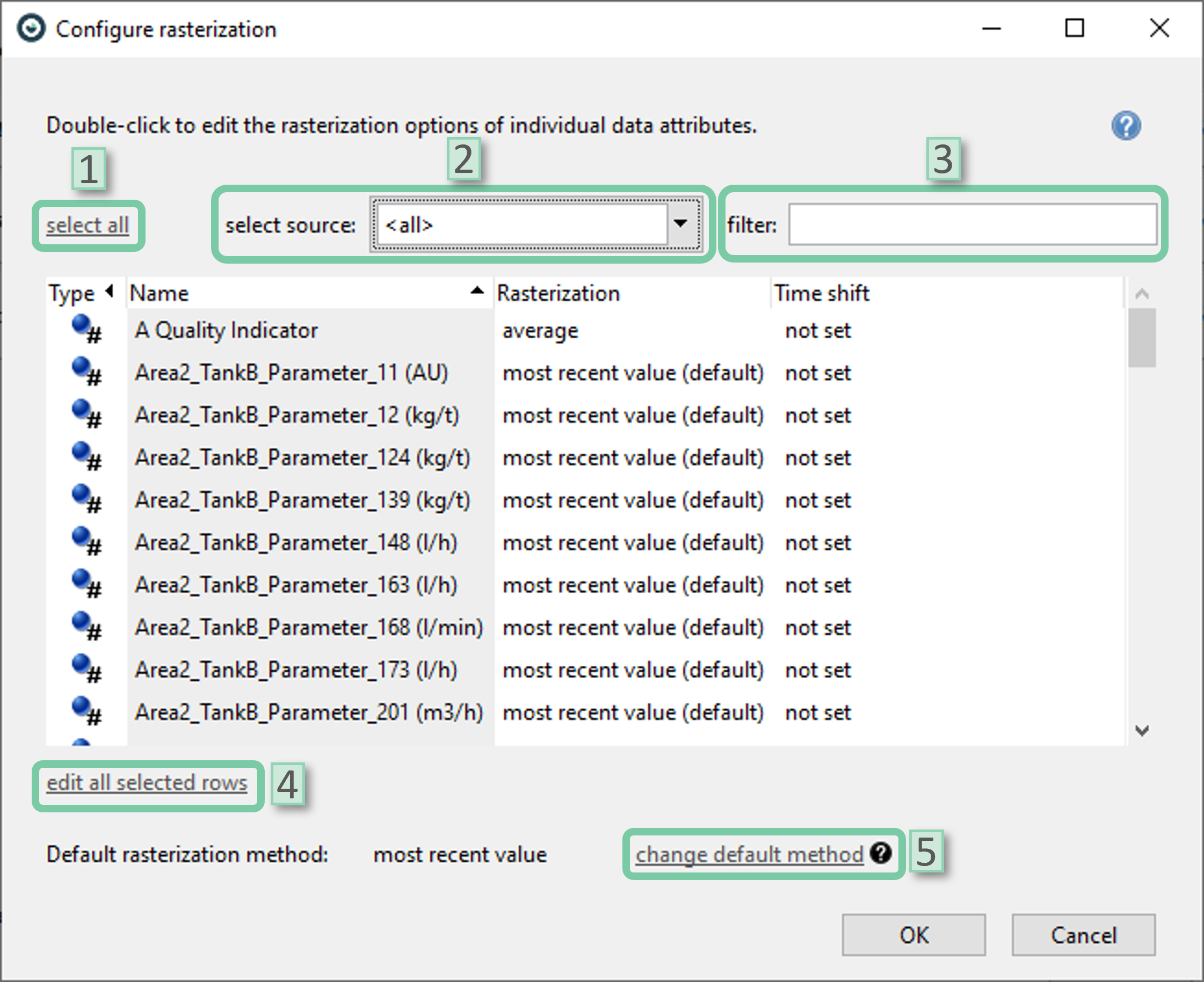
The user can double-click on any data attribute to change its rasterization settings. Selecting multiple data attributes by holding the ‘ctrl’ key while clicking is also possible.
- Select all: Selects all data attributes in the list below.
- Select source: The user can filter the attributes shown by selecting data source(s). This is beneficial if the user wants to assign different rasterization methods per source, as only some methods are available for all types of time interpretations.
- Filter: The user can filter the data attributes by name using this bar.
- Edit all selected rows: Pops up the ‘Edit rasterization options’ window for editing the rasterization options of selected attributes. If multiple data attributes from sources with different time interpretations are set, only common rasterization methods available for all selected time interpretations will be offered.
- Change default method: Pops up the ‘Default rasterization methods’ window to edit the default rasterization options of selected attributes.
Edit rasterization options
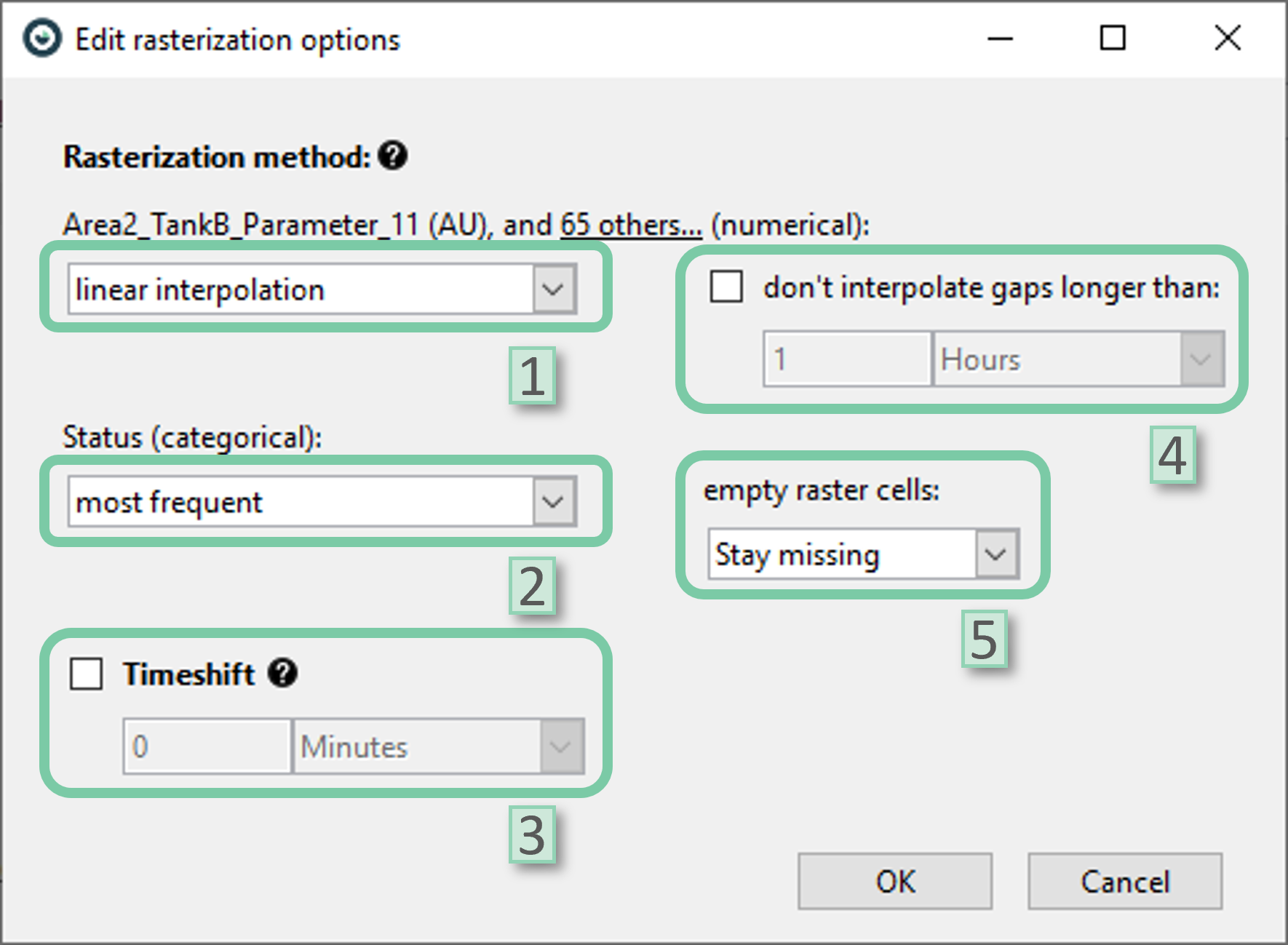
- Rasterization method for numerical attributes: Sets the interpolation method for numerical attributes. Only available if the selection involves at least one numerical data attribute.
- Rasterization method for categorical attributes: Sets the interpolation method for categorical attributes. Only available if the selection involves at least one categorical data attribute.
- Timeshift: The user can introduce a lead or lag for all selected attributes.
- Don’t interpolate longer than: The user can set whether the long gaps should be interpolated during rasterization. Gap duration could be specified. Note that this setting is only available if an interpolation method is selected as the rasterization method.
- Empty raster cells: The user can specify if the raster spans without data should stay missing or be set to zero. Note that this setting is only available if an aggregation method is selected as the rasterization method.
Default rasterization methods
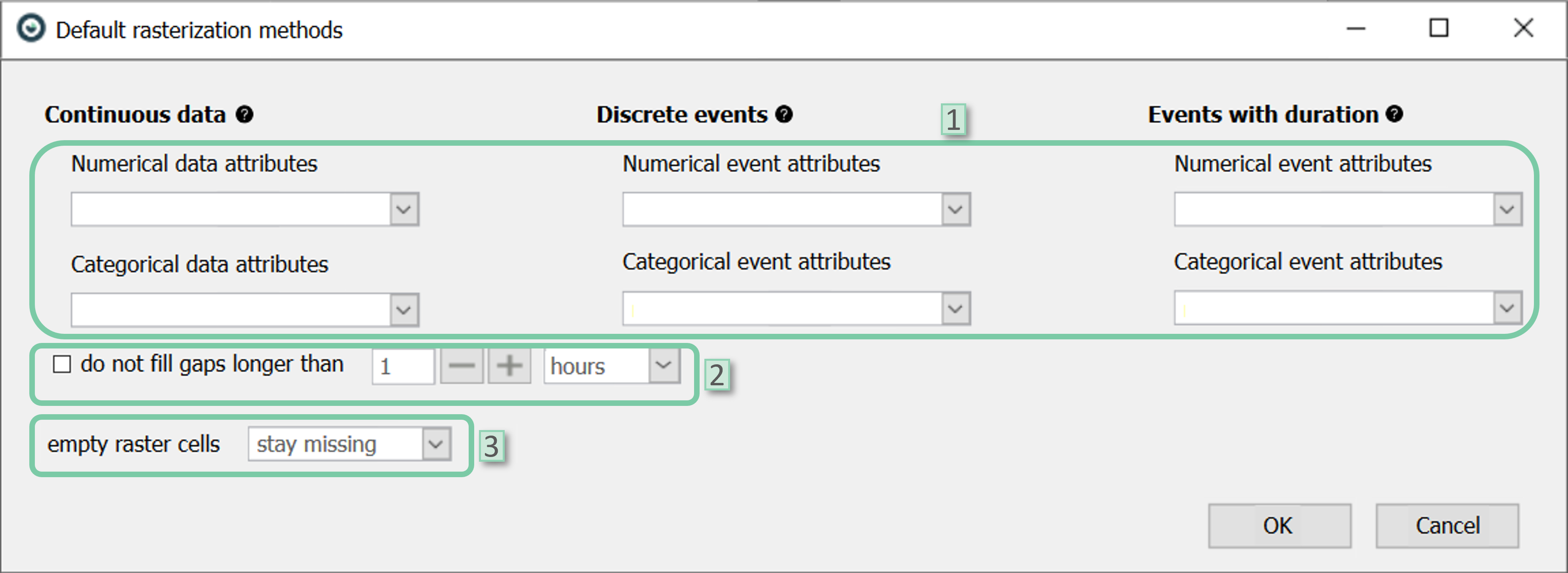
- Rasterization methods: The user can select the default rasterization methods for each time interpretation and attribute type combination. There could be six selections at maximum as Visplore offers three time interpretations (discrete, continuous, and events with durations) and 2 data attribute types (numerical, categorical). However, please note that the selections are only shown if these combinations are present in the currently loaded data.
- Don’t interpolate longer than: The user can set whether the long gaps should be interpolated during rasterization. This is a global setting for all attributes that apply.
- Empty raster cells: The user can specify if the raster spans without data should stay missing or be set to zero. This is a global setting for all attributes that apply.
The available rasterization methods depend on the time interpretation of the data source. This can be changed in the Data Source Manager if desired. Below is a table depicting available rasterization methods for different time interpretations and data type combinations.
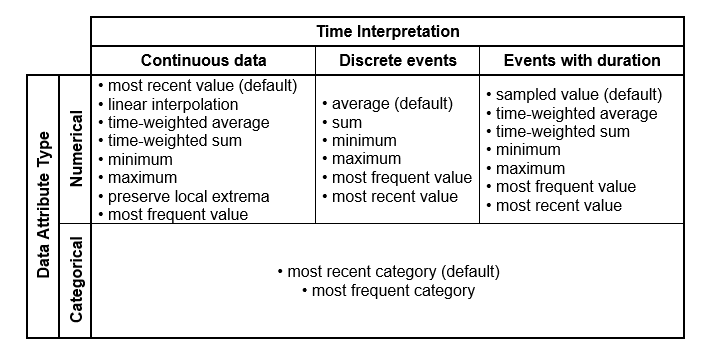
- Most recent value: Returns the most recent value.
- Most frequent value: Returns the most frequently occurred value over the raster span. Selects the chronologically first appeared value if multiple values have the same frequency.
- Linear interpolation: Returns a value for the rastered data record using the closest original data records’ values by linearly interpolating the duration in between.
- Time-weighted average: Returns the weighted average of the neighbouring data records w.r.t. new raster span.
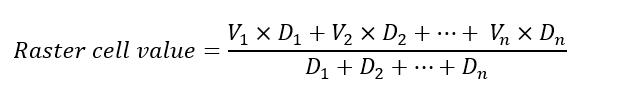
Where, Vn is the value of nth data record, and Dn is the duration of nth data record that falls into the span of the rastered data record.
- Time-weighted sum: Assigns values to the intervals in a way that maintains the sum over the original timespan. In the case of a smaller raster spans than the original temporal resolution, each interval in the rastered time-series is assigned a value that is a time-weighted fraction of its original value, proportional to the ratio of the rastered interval duration to the original interval duration. Conversely, the raster method effectively becomes a regular sum for a larger raster than the original temporal resolution. This means that if the resampled interval duration is larger than the original interval duration, the value assigned to each interval in the resampled time series would be the sum of the corresponding original intervals.
- Minimum: Returns the minimum of the values over the raster span.
- Maximum: Returns the maximum of the values over the raster span.
- Preserve local extrema: Returns the extrema point within the raster span. This is useful if the aim is to retain the information carried by the extreme values.
- Average: Returns the average of the values over the raster span.
- Sum: Returns the sum of the values over the raster span.
- Sampled value: Returns the value present at the raster cell’s timestamp.
